Speech clarity
Speech clarity concerns the quality of speech transfer to the listeners. In a reverberant room with disturbing background noise, it can be difficult to pick up speech.
Unclear
Clear

The sound that reaches the listener first is called direct sound. This is followed by early reflections. The early reflections that reach the listener within 50 ms are integrated with the direct sound and thus have a positive effect on speech clarity. The reflections that come later may be perceived as disturbing.
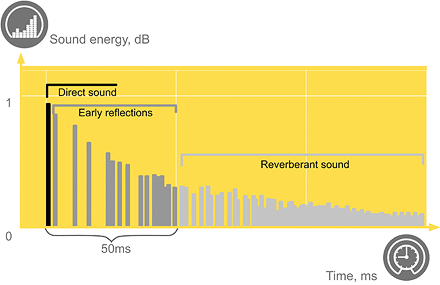
The Clarity measurement (C50) compares the sound energy in early sound reflexes with those that arrive later. A high value is positive for speech clarity.
In the case of poor speech transmission, variations in speech are perceived less well. Factors that impair speech transmission, thus contributing to a lower STI index are, for instance, background noise, long reverberation and echoes. When speech transmission is perfect, STI = 1. In a normal-sized classroom, STI should be greater than 0.75.

Bad speech transmision.
Good speech transmision.
|
Perceived attribute |
Objective descriptor |
Designation |
Unit |
Explanation |
Standard |
|
Speech clarity |
Speech clarity |
C50 |
dB |
Measures effect of the room’s early reflections. This is important for speech clarity. |
ISO 3382-1 |
|
Speech clarity |
Speech Transmission Index | STI | Index (0-1) | Measures quality of speech transfer from speaker to listener. | IEC 60268-16 |
